 23 July 2024
23 July 2024
Minako Morita-Jaeger is Policy Research Fellow at the UK Trade Policy Observatory, a researcher within the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy (CITP) and Senior Research Fellow in International Trade in the Department of Economics, University of Sussex. She currently focuses on analysing UK trade policy and its economic and social impacts.
The UK is a services economy which accounts for 81% of output (Gross Value Added) and 83% of employment.UK services exports (£470 billion in 2023) are the world’s second largest after the US and 75% of its services exports are digitally delivered. The UK is ranked as world-leading in terms of data governance. Under the new Labour government, it is time to take the initiative on data flow governance at the global stage to achieve a sustainable and accountable digital environment. With the set back in the US negotiations on free data flows at the WTO, the UK can take the initiative to collaborate with the EU and Japan.
The EU-Japan EPA, which entered into force in 2019, lacked provisions on free data flows and personal data protection. This has now been addressed with the signing of the new protocol on 31 January this year which is incorporated into the EU-Japan EPA. The new EU-Japan protocol can be seen as game changers. First, they strike a balance between free data flows and legitimate public policy objectives. Under Article 8.81, measures that prohibit or restrict cross-border data flows, such as localisation requirements of computing facilities or network elements, are restricted. These provisions are similar to the existing digital trade provisions under FTAs/digital trade agreements led by the Asia-Pacific countries, such as the CPTPP.
Yet a significant difference with the Asia-Pacific style FTAs is the scope and definition of “legitimate public policy objective” (Art. 8.81.3 and its footnotes). The new protocol reflects the EU’s approach under the UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA) which provides more detail compared to the Asia-Pacific led digital trade agreements.
Another striking difference is that personal data protection is set as a fundamental right. The provisions regarding cross-border data transfers go together with the new provisions regarding protection of personal data (Art. 8.82). The clause is comprehensive and could be seen as the highest standard among existing digital trade agreements, including the EU-UK TCA. It underlines the importance of maintaining high standards of personal data protection to ensure trust in the digital economy and to develop digital trade. Such deep commitments between the EU and Japan were enabled by ongoing policy dialogues, including the EU-Japan Digital Partnership Council.
An interesting aspect here is Japan’s policy journey on digital trade agreements, which reflects a shift from the US or Asia-Pacific style pro-trade approach to the EU-style human-centric approach. The starting point of Japan’s policy journey was the CPTPP e-commerce chapter (originally the TPP e-commerce chapter) which strongly reflected US tech-companies’ desire for a laissez-faire international digital environment. The agreement prioritises free data flows with a very narrow public policy space. Under the Japan-US Digital Trade Agreement (DTA), the Japanese government accepted the US approach, which leans even more towards business interests than the CPTPP.
Subsequently Japanese policy preference shifted more towards the EU’s human-centric approach. The Japan-UK Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) signed October 2020, which reflects both the CPTPP and the EU-UK TCA, could be seen as a first step in this direction.
Why the change? At the domestic level, data privacy regimes have been legally and institutionally strengthened over the last decade. At the international level, the Japanese government has been advocating the new norm of “Data Free Flow with Trust” from 2019 through G7, G20, OECD and beyond.[1] The Japanese government considers that the new EU-Japan protocol, incorporating the principle of “DFFT”, will contribute to a more balanced approach to digital trade and could become a model of a 21st century digital trade agreement.
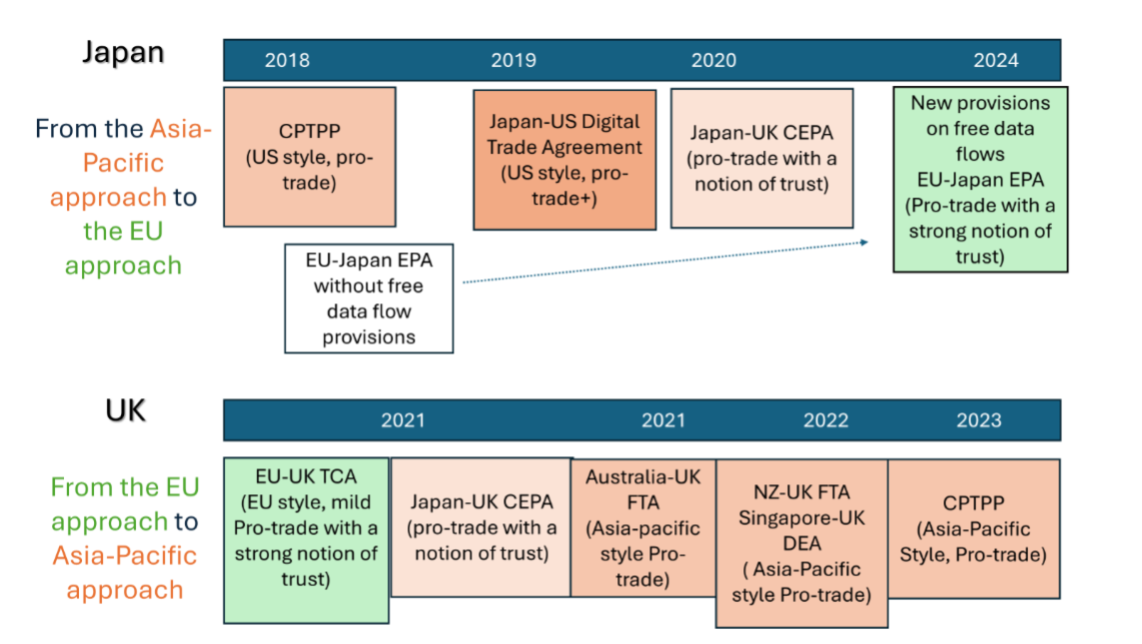
In contrast, the UK’s policy journey has unfolded in the opposite direction (Figure 1). Other than the EU-UK TCA, the UK has tended to depart from the EU style digital governance approach. With the tilt to the Indo-Pacific, the UK has aligned itself more to the Asia-Pacific style market-driven approach to digital trade governance. The digital trade rules under the Australia-UK FTA, UK-New Zealand FTA, and Singapore-UK DEA are modelled on the CPTPP.
Indeed, the Conservative UK government’s efforts to reform of the UK data protection regime (Data Protection and Digital Information Bill), reflects a drift away from EU-style data governance. It has also enabled the UK to strike these digital trade deals. The reforms prioritised data-driven innovation with an ambition of making the UK an international data hub, but legal experts raised concerns over their ethical, social and legal implications.
The Labour Party manifesto was silent about digital trade governance, and the approach of the new government to digital trade is an important question as it will, in part, shape tomorrow’s world.
At the multilateral level, we have entered a new phase of negotiations. It seems that cross-border data flows provisions are being dropped from the on-going WTO Joint Statement Initiative (JSI) negotiations on e-commerce. This is because of the lack of support, if not opposition, from the US as it wants stronger tech regulation. Although there was not a consensus over the balance of free data flows and public policy objectives even before the US’s objections, the US’s position has proved a key obstacle to multilateral rules on data flows. Under such circumstances, promoting a new digital trade model like the EU-Japan new agreement and the UK-EU TCA could help mitigate US’s concerns over limited public policy space.
The quality of the UK’s data governance is ranked as world-leading according to the Global Data Governance Mapping Project. This means that the UK is well positioned to show the best practice to its trade partners while enhancing the trust side of digitisation and promoting digital trade at the bilateral, plurilateral and multilateral levels.
With the new UK government, there is an opportunity to revisit its role at the international level. Given that the Labour government values individual / human rights while promoting innovation, the UK could play an active role in forging a broader consensus on the balance between free data flows and public policy space. As part of it, it seems natural for the UK to collaborate with Japan and the EU to promote the balanced approach achieved under the EU-UK TCA and the EU-Japan EPA. This could help regain support from the US administration for the WTO negotiations and other international forums.
[1] As for “DFFT” and its relation with trade policy, see “Can trade policy enable “Data Free Flow with Trust?“
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.