 18 June 2024
18 June 2024
Alasdair Smith is a UKTPO Research Fellow, a researcher within the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy (CITP), Emeritus Professor of Economics and Former Vice-Chancellor at the University of Sussex.
The 2019 General Election focused on the one issue of Brexit, and Boris Johnson’s victory enabled the UK to leave the EU. The evidence analysed by UKTPO and many others since then has confirmed the general expectation among expert economists at the time that Brexit would have negative economic effects. And recent opinion poll evidence is that a majority of voters think Brexit was a mistake.
To say that Brexit was a mistake does not imply it could or should be simply reversed. Yet, it is reasonable to expect the political parties to address the issue in their current election campaigns.
The Labour Party’s ambition for the future EU-UK relationship is set out in two paragraphs in their manifesto published on 13 June:
“With Labour, Britain will stay outside of the EU. But to seize the opportunities ahead, we must make Brexit work. We will reset the relationship and seek to deepen ties with our European friends, neighbours and allies. That does not mean reopening the divisions of the past. There will be no return to the single market, the customs union, or freedom of movement.
Instead, Labour will work to improve the UK’s trade and investment relationship with the EU, by tearing down unnecessary [my emphasis] barriers to trade. We will seek to negotiate a veterinary agreement to prevent unnecessary border checks and help tackle the cost of food; will help our touring artists; and secure a mutual recognition agreement for professional qualifications to help open up markets for UK service exporters.”
A firm commitment to stay out of the EU for the next Parliament is surely wise. The UK-EU relationship has been bruised by the experience of the last 8 years. Rebuilding the relationship will take time and patience, and the opportunity to solidify the long-term relationship lies some way in the future. The incoming government faces formidable challenges in many areas and even a long-term plan to rejoin the EU would be a diversion from more immediate priorities.
Since there is no plan to rejoin, it follows that a new government must indeed seek to “make Brexit work”. It’s also right to aim for the removal of any unnecessary border checks and other barriers to trade that have damaged the UK economy.
This is a more positive and less dogmatic approach to the UK-EU relationship than the Conservative manifesto whose main concern is to rule out “dynamic alignment” to EU rules and “submission to the CJEU [the Court of Justice of the EU]”.
Dynamic alignment means sticking to EU rules even when they change. There’ s a strong case for dynamic alignment in many areas, to create a climate of regulatory predictability in place of the regulatory uncertainty and instability of recent years. In any case, firms have to satisfy EU regulations for products they sell in the EU. In many important sectors of the economy (like chemicals and motor vehicles) that means virtually all their production has to meet EU requirements, so separate UK regulations are a deadweight cost.
The Labour manifesto’s red lines are clearly drawn: “no return to the single market, the customs union, or freedom of movement”. The political pressure for such clear lines is understandable. However, they will constrain the objective of reducing border checks and other barriers to trade.
The European single market (which encompasses some non-EU countries like Norway) is the regulatory framework which removes barriers to trade within Europe. Members of the single market adopt common regulations, common processes for assessing conformity with these regulations, and a common legal framework under the umbrella of the CJEU. Members of the customs union similarly have a common policy towards goods imported from non-member countries. Checks on trade between EU countries are unnecessary.
However, if the UK remains outside the single market and the customs union, checks on UK exports to the EU are necessary to make sure that EU rules are satisfied. It’s not enough for UK producers to satisfy EU rules – their products still need to be checked for conformity. However much trust and goodwill are built up with our EU partners and no matter how much alignment there is with EU rules, the scope for removing “unnecessary” barriers to UK-EU trade may be frustratingly limited in practice.
The main political barrier to UK membership of the single market is, of course, the additional single market requirement for the free movement of labour. But post-Brexit restrictions on labour mobility between the EU and the UK has had adverse effects in many important UK sectors: including business services, agriculture, hospitality, social care, and the creative industries.
It’s understandable that the Labour manifesto rules out free movement, but notable that it is silent on the recent EU offer on youth mobility: proposals which emphatically do not imply freedom of movement (not least because they involve visa controls). These proposals would restore to young Europeans in the UK and the EU some of what they lost as a result of Brexit, and would also help address some of the problems of the sectors most affected by Brexit. Surely an incoming government should take a more positive approach to the EU offer.
Opinion poll evidence is that a clear majority of the UK electorate favour a return to EU-UK freedom of movement. A new government may find the political constraints changing quite quickly, so that rejoining the single market becomes thinkable.
A manifesto commitment not to rejoin the single market applies to the next Parliament but doesn’t stop the government from preparing to rejoin in the following Parliament. The path to re-entering the single market would in any case be a long one, probably via the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) into the European Economic Area (the EEA). This path requires preparation and negotiation.
That preparation should include addressing the fact that the single market requires free movement of labour not free movement of citizens. The UK could develop rules for a regime in which EEA citizens are not unconditionally free to come to the UK but are free to relocate to the UK (with their families) in order to work.
The Liberal Democrat manifesto, in contrast to the Labour manifesto’s red lines, makes a positive commitment to rejoining the single market:
“Finally, once ties of trust and friendship have been renewed, and the damage the Conservatives have caused to trade between the UK and EU has begun to be repaired, we would aim to place the UK-EU relationship on a more formal and stable footing by seeking to join the Single Market.”
Realistically, the timetable suggested by these words could well extend beyond the 4-5 years of the next Parliament. In this case, the difference between the Labour and LibDem manifestos may be presentational, rather than real. The single market issue will not go away, even if it cannot be settled before another general election at which a proposal to rejoin the single market could be put to the electorate.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher June 18th, 2024
Posted In: Uncategorised

 30 May 2024 – I
30 May 2024 – I
 ngo Borchert is Deputy Director of the UKTPO, a Member of the Leadership Group of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy (CITP) and a Reader in Economics at the University of Sussex. Michael Gasiorek is Co-Director of the UKTPO, Co-Director of the CITP and Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex. Emily Lydgate is Co-Director of the UKTPO and Professor of Environmental Law at the University of Sussex. L. Alan Winters is Co-Director of the CITP and former Director of the UKTPO.
ngo Borchert is Deputy Director of the UKTPO, a Member of the Leadership Group of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy (CITP) and a Reader in Economics at the University of Sussex. Michael Gasiorek is Co-Director of the UKTPO, Co-Director of the CITP and Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex. Emily Lydgate is Co-Director of the UKTPO and Professor of Environmental Law at the University of Sussex. L. Alan Winters is Co-Director of the CITP and former Director of the UKTPO.
A general election is underway, and the parties are making various promises and commitments to attract voters, and both the main parties – the Conservatives and Labour – are keen to persuade the country that they have a credible plan. Now it might just be that the authors of this piece are trade nerds, but one key aspect of economic policy has not yet been clearly articulated, or even mentioned – and that is international trade policy.
In our view, this is a mistake. As a hugely successful open economy, international trade constitutes a significant share of economic activity, supports over 6 million jobs in the UK, spurs innovation, and enhances consumption choices. In short, trade and investment flows are an important element in leading to higher economic growth and welfare. In addition, trade and investment relations intertwine considerably with increasingly fraught geopolitics. Against this backdrop, the UK cannot afford to give trade policy short shrift.
Admittedly, though, trade policy is complex. It is also, more than ever, linked to other dimensions of public policy – and that does make it harder to have simple soundbites. That is no doubt part of the explanation why trade hasn’t been mentioned. The other part is that discussions of trade policy are closely intertwined with the ‘B’ (Brexit) word, and those discussions have become somewhat toxic.
Nevertheless, we argue that sound trade policy is a high priority for the UK. Listed below are some practical, feasible, and specific policy proposals that would help to ensure a better and more coherent UK trade policy, and thus lead to more equity in trade outcomes as well as higher rates of economic growth for the UK.
Process and consultation
1. Publish a Trade Strategy, which should elucidate principles as well as concrete policy objectives and intentions. Recognise the importance of both goods and services trade policy for the UK economy, nationally and across the regions.
2. Reduce executive power over trade policy, through establishing an independent Board of Trade, strengthening Parliamentary oversight over Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and improving consultative processes with devolved nations and with stakeholders in trade.
3. Ensure and commit to transparency in UK trade data, good access to data for researchers and be transparent about the analyses undertaken by government.
Policy Areas:
4. Plurilateral / Multilateral / World Trade Organization (WTO):
a. Ensure that UK trade policy remains consistent across its various partner countries and across the different free trade agreements notably with regard to regulatory approaches.
b. Ensure that trade policy supports the rules of the multilateral trading system. Work on policy areas, such as supply chain security, bilaterally and multilaterally in ways which are at a minimum consistent with this, if not designed to strengthen multilateral cooperation.
c. In the absence of an effective WTO dispute settlement mechanism, join the Multi-party Interim Appeal Arbitration Arrangement (MPIA).
5. Bilateral trade relations:
a. Do not expect too much from further, notionally comprehensive, free trade agreements with more countries. Focus more on improving the workings and utilisation of existing agreements.
b. Work to reduce costs of trade with the EU in both goods and services, e.g. by mutual recognition agreements on standards, qualifications and certification and negotiating an EU-wide youth mobility scheme. As a first step seek a veterinary agreement.
c. Seek to cooperate with the EU on environmental regulation that impacts upon trade, most immediately by linking ETS schemes with the EU and introducing a compatible CBAM.
d. Review rules of origin with the EU and seek improvements where there may be benefits to both parties (eg. Electric vehicles and car batteries).
6. Domestic:
a. Provide better resourcing and introduce more robust border checks to uphold the UK’s high food standards and prevent the introduction of pest and animal diseases.
b. Work closely with industry to make sure that the implementation of new border arrangements, including the Border Target Operating Model and the Windsor Framework/UK internal market, are understood by businesses and don’t create perverse incentives to UK internal trade, imports or exports. SMEs are likely to face particular challenges.
c. Have a clear digital strategy which deals both with the digitisation of trade transactions and processes, and the rise in digital trade. This strategy should set out the balance of objectives with regard to consumer protection, cyber security, and competitiveness.
This is by no means intended as a comprehensive list, but focusses on some key principles, and specific priorities which are feasible, would make a difference, and could be immediately focussed on. When the manifestos are published it will give an opportunity to assess the parties’ approaches to trade policy and to see whether proposals go beyond broad statements of intent by providing practical details and commitments in line with any of the above.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or the UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher May 30th, 2024
Posted In: UK - Non EU, UK- EU
Tags: Brexit, General Election 2024, trade policy, UK Election
Share this article: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 22 May 2024
22 May 2024
David Henig is Director of the UK Trade Policy Project at the European Centre for International Political Economy (ECIPE). He has written extensively on the development of UK Trade Policy post Brexit, in the context of developments in EU and global trade policy on which he also researches and writes. L. Alan Winters is Co-Director of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy (CITP) and former Director of the UKTPO.
One of the most heralded claims for Brexit was taking back control of UK international trade policy. Four years later, this is not widely seen as having been a success. Trade growth has been disappointing, the UK has become less open, exporting is still heavily concentrated in the Southeast of England, and there is little trust in Government pronouncements on trade. And yet there is almost no coherent discussion of trade policy and no evident strategy guiding future policy objectives or the signature of new trade agreements.
Part of the issue is that thinking about trade policy is trapped in the remnants of the Brexit debate and substantially seen in party political terms; it is consequently lacking any broadly accepted understanding. This is unsatisfactory and as part of the solution we propose to return the UK Board of Trade to its former status as a centre of excellence offering advice to the government and a source of impartial public information on international trade policy. Our paper is not the first to suggest that the Board of Trade be revived from its current somnolence, but it is the first to propose some details and a road map for that revival.
Our restructured Board of Trade would be a non-departmental public body – a well-established form for similar functions offering public service where there is a significant advantage of operational independence. It would be largely independent of government but nonetheless, work alongside government and all stakeholders to significantly elevate the UK’s trade policy debate and trade performance.
What would a restructured Board of Trade do?
The Board’s most prominent task would be to produce an annual report on UK trade performance and assess major new trade-related policies including trade agreements. This would be produced after extensive consultation with stakeholders and would be made public in an accessible form and debated in Parliament.
The Board would provide two impact evaluations of major prospective free trade agreements (FTAs), one at the stage of conception to see if it was worth pursuing and what the negotiating mandate should be (as the government currently does), and one close to completion of the negotiations, which would provide public information and sufficiently detailed analysis to allow Parliament to have an informed debate about whether to ratify the agreement. (Improved Parliamentary scrutiny of FTAs would be a second element of our improvement plan.) The Board would also conduct ex post evaluations of previous agreements in order to optimise them and learn lessons for the future.
Many modern trade problems concern regulation and trade, particularly in services. For example, there is a growing body of trade and climate change regulation, where there will be impacts both on trade and wider policy objectives. The Board would be required to consider major interfaces between trade and regulation, explaining them to the public and policymakers and helping with solutions.
Finally, we envisage a series of reports on specific trade and trade policy developments. These may include both detailed exercises to underpin future policy and simple explainers for the interested public.
Underpinning the Board’s work, there should be substantial and substantive engagement with Parliamentarians, stakeholders and the public. This would be partly aimed at improving policy and policymaking by encouraging a broad range of inputs, but also at building confidence that the UK had a satisfactory and inclusive approach to trade.
A model for a restructured Board of Trade
The challenge in designing a new Board of Trade is to create a balance between expertise/experience, independence from government, stability in the long-term policy vision and the fact that government, and to a lesser extent Parliament, must have a material role in the composition of a body with which they are intended to work closely. We suggest one model but recognise that others are possible.
Maintaining good relations between the Board and the government will be necessary for the former’s success. Hence, in our model, the relevant Secretary of State would continue to be termed the President of the Board of Trade and should appoint the members of a small politically balanced Board. These would have input to the Annual Report and formally receive it.
The main leadership of the Board’s work, however, would come from a Trade Council, with broad representation and expertise/experience in trade (not just exporting!). The Secretary of State would appoint the Council Chair in consultation with the relevant Parliamentary Committees and also a few members of a Trade Council. The majority of the Council would be nominated by the Chair and the whole Council approved by the small formal Board. The Chair would also appoint a Chief Executive Officer to lead the day-to-day work having consulted the Chairs of the relevant Parliamentary Committees.
The reconfigured Board of Trade should be established in legislation and have a guaranteed role in informing Parliament. It could, however, be created in shadow form virtually as soon as a government desired it, with formal statutory establishment following later.
By looking at similar UK institutions and the Swedish National Board of Trade, we estimate that the Board might require a staff of around 90 and an annual budget of about £10 million. At least some of these would come from the transfer of existing functions and staff from inside government. Lest this seems like a lot in our current straitened circumstances, recall that around one-third of UK consumption and investment comes from imports and around one-third of output is exported.
Getting trade right is important! Our proposal fills what is an obvious gap in current arrangements, with a view to building the broad consensus that is essential to a successful trade policy.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher May 22nd, 2024
Posted In: UK- EU
Share this article: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
 23 April 2024
23 April 2024
Adriana Brenis is a Research Fellow of the UK Trade Policy Observatory (UKTPO) at the University of Sussex Business School. She holds an MSc in Business, Finance and Economics and a PhD in Economics from the University of Sheffield. Adriana’s research focuses on international trade, economic policy analysis and innovation.
The UK government recently announced its plan to implement common user charges for imports coming into the country. This has generated some controversy and, just this week, rumours that the government may again suspend the introduction of elements of the new Border Target Operating Model (BTOM).
The common user charges, set at a flat rate of £10 or £29 per commodity line, are capped at 5 charges per consignment, resulting in a maximum fee of £145. These charges will be applied to low-risk products of animal products (POAO), medium and high-risk animal products, along with plants and plant products. Initially, they will only be collected at border controls in Dover and Eurotunnel starting April 30th. This is part of the new BTOM system, aimed at improving border procedures. The goal is to cover the expenses of running these border facilities while protecting the UK’s food supply, farmers and the environment from diseases that could come in through these routes.
This blog explores the significance of these ports in facilitating the importation of goods into the UK and examines the extent to which the announced charges may affect incoming shipments.
Our calculations suggest that the animal and plant products that could face common charges represent about £38 billion of imports into the UK, making up 6% of all UK imports. Among these, 5.8% represent animal products and 0.2% plant products. Table 1 shows that 78% of these ‘at risk’ imports come from the EU, while 22% are from other parts of the world.
| Products at risk | EU | Non – EU | Total |
| Animal | 28.68 | 8.18 | 36.86 |
| Plants | 1.22 | 0.24 | 1.46 |
| Total | 29.90 | 8.41 | 38.32 |
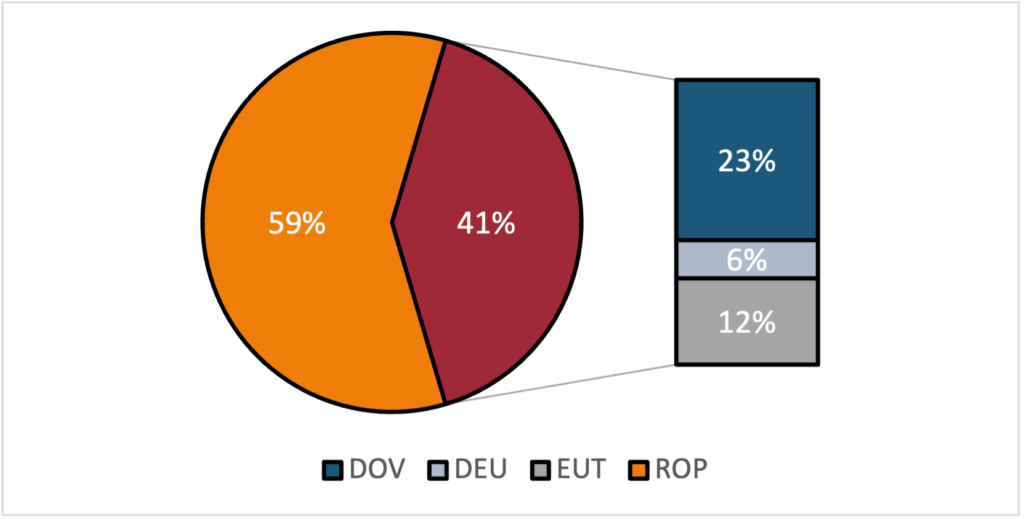
Given the substantial proportion of animal imports from the EU, we examine what share passes through the controlled borders – where the common user charges will be implemented starting April 30th. As illustrated in Figure 1, of the eligible animal products subject to charges (£28.7 billion), 41% (£11.7 billion) are imported through the controlled borders of Dover (DOV), Eurotunnel (EUT), and Dover/Eurotunnel (DEU), while the remaining 59% come through other ports in the UK (ROP). Among these, Dover stands out as the primary port for imports at 23%, followed by 12% via Eurotunnel, and 6% through Dover/Eurotunnel.
Source: HMRC and Animal & Plant Health Agency (2023)
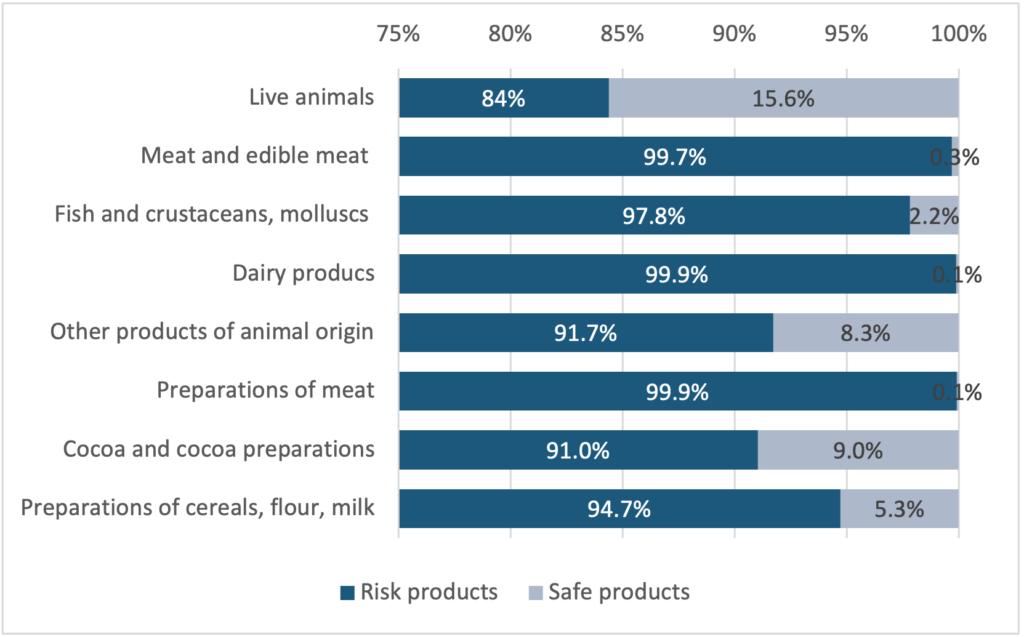
Among the different types of animal products classified under the Harmonized System (HS) at the 2-digit level, 31 out of the total number of 97 HS chapters have a percentage of animal products that could be subject to charges. Figure 2 highlights the HS classification at a 2-digit level, with the highest percentage of imported animal products at risk. Particularly, almost all imported products in HS 02 “Meat and edible meat”, HS 04 “Dairy products”, and HS 16 “Preparations of meat” are at risk. Other sections with more than half of their imported products at risk include HS 21 “miscellaneous edible preparations” (73%), and HS 23 “Residues and waste from the food industry” (75%). In addition, 91% of imported products in HS 18 “Cocoa and cocoa preparations” and 95% in HS 19 “Preparations of cereals, flour, starch or milk” could face charges, depending on whether they contain products of animal origin (POAO).
Source: HMRC and Animal & Plant Health Agency (2023)
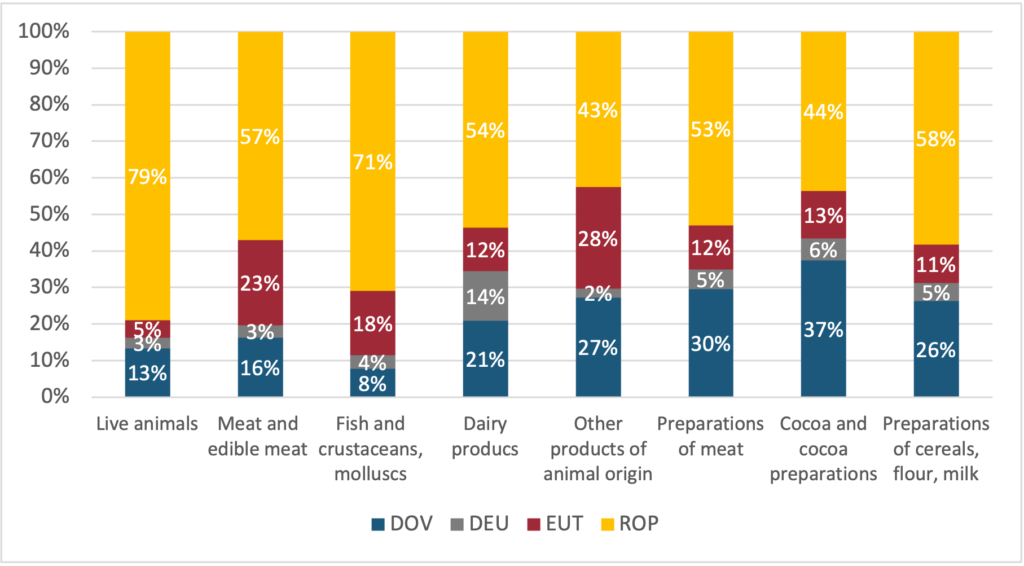
Focusing on the eight sections where most imports face potential fees, Figure 3 illustrates the share of the imports coming through the ports where charges apply. Live animals and fish, crustaceans and molluscs mainly come through other ports (79% and 71% respectively). In contrast, other products of animal origin primarily come through fee-charging ports, with Eurotunnel (EUT) at 28%, and Dover (DOV) at 27%. Similarly, cocoa and cocoa preparations products mostly enter through ports with charges, with 37% through Dover. Moreover, a large proportion of meat and edible meat (43%), dairy products (46%), preparations of meat (47%), and preparation of cereals, flour, and milk (42%) are brought in through these controlled borders with fees.
Source: HMRC and Animal & Plant Health Agency (2023)
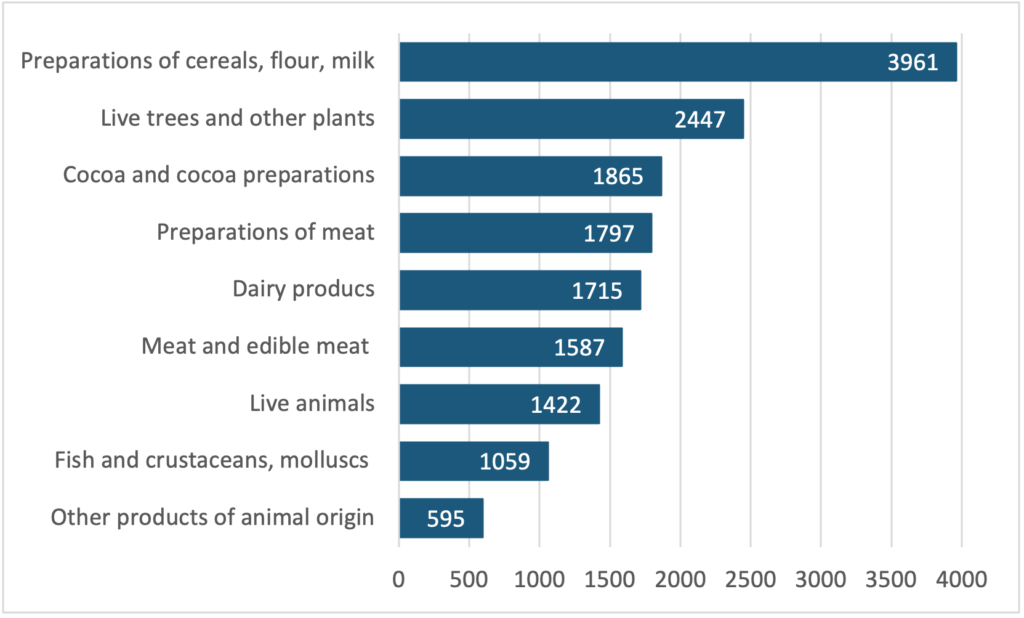
In 2023, out of the total Great Britain firms importing products globally (248,445 firms), those importing goods at risk from both EU and non-EU countries accounted for 16%, totalling 40,619 firms. Figure 4 provides the number of firms primarily importing within these eight categories, along with plant products from both EU and non-EU countries. The figure shows a significant number of firms fall within preparations of cereals, flour, and milk, followed by live trees and cocoa and cocoa preparations. As seen in Figure 3, these two categories – cocoa and cocoa preparations, as well as preparations of cereals – show a considerable percentage of imports arriving through the charged ports of Eurotunnel and Dover. Consequently, many of these firms could be affected by the upcoming common user charges starting on April 30th.
Table 2 provides a detailed view of the number of firms importing large amounts of animal and plant products within these categories. Considering the sections with high percentages of animal imports arriving through charged ports, like other products of animal origin and cocoa preparations, along with those with substantial imports (such as meat, dairy, and cereal preparations) are also, products like animal products n.e.s, including fresh cheese, pizzas, chocolate and other cocoa preparations, and sausages, which could be among the most affected.
Source: HMRC and Animal & Plant Health Agency (2023)
| 8-digi level | Name | Number of Firms |
| 01012100 | Pure-bred breeding horses | 859 |
| 02013000 | Fresh or chilled bovine meat, boneless | 390 |
| 03047190 | Frozen fillets of cod “Gadus morhua, Gadus ogac” | 101 |
| 04061050 | Fresh cheese “unripened or uncured cheese”, incl. whey cheese and curd | 258 |
| 05119985 | Animal products, n.e.s.; dead animals, unfit for human consumption | 351 |
| 06029050 | Live outdoor plants, incl. their roots | 761 |
| 16010099 | Sausages and similar products of meat | 609 |
| 18063100 | Chocolate and other preparations containing cocoa | 368 |
| 19059080 | Pizzas, quiches and other bakers’ wares | 1370 |
The introduction of common user charges for imports (especially for firms dealing with products subject to these fees) could have significant implications for both businesses and consumers. For firms, particularly those importing goods through charged ports, there may be a notable increase in operational costs due to the additional charges incurred. This could potentially impact their profitability and competitiveness. Additionally, firms may need to reevaluate their supply chain strategies, potentially exploring alternative ports or sourcing options to mitigate the impact of fees. Furthermore, the rise in costs could prompt changes in consumer behaviour, with some individuals opting for alternative imported products not subject to fees. Overall, the implementation of common user charges has the potential to reshape import dynamics, affecting both firms and consumers alike.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher April 23rd, 2024
Posted In: Uncategorised
Share this article: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

 23 February 2024
23 February 2024
Peter Holmes is a Fellow of the UK Trade Policy Observatory and Emeritus Reader in Economics at the University of Sussex Business School. Sunayana Sasmal is a Research Fellow in International Trade Law at the Observatory.
The World Trade Organization (WTO) dispute settlement system is in crisis. Here, and in a comprehensive working paper, we discuss one potential solution to one of the many issues confronting it. Non liquet is a legal principle that allows a tribunal to decline rendering a ruling when there is no law. We think this concept could partially address the major issue of judicial overreach. But first, some background.
Charlotte Humma February 23rd, 2024
Posted In: Uncategorised
16 February 2024

 Michael Gasiorek is Director of the UK Trade Policy Observatory and Co-Director of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy. He is Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex Business School. Nicolo Tamberi is Research Fellow in Economics at the University of Sussex and Fellow of UKTPO.
Michael Gasiorek is Director of the UK Trade Policy Observatory and Co-Director of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy. He is Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex Business School. Nicolo Tamberi is Research Fellow in Economics at the University of Sussex and Fellow of UKTPO.
HMRC has just published statistics for trade in goods for December 2023, giving us three years of data after the implementation of the Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA) with the EU in 2021. This blog reviews trends in UK trade with the world and the effects of the TCA on UK-EU trade.
There is good and bad news for UK trade in goods. Starting with the bitter pill, the UK’s trade in goods with the world has underperformed compared to other comparable countries over the last few years. Figure 1 shows the exports (panel a) and imports (panel b) of the UK, marked in red, and other OECD countries in blue, together with the series for the OECD total in dark blue. While during the period 2013-16, the UK was in line with the OECD total, the UK’s imports and exports started to slow down since the Brexit referendum in June 2016. For exports, the gap with the OECD total increased substantially with the Covid-19 pandemic. Imputing causation in this setting is not easy; most likely, the Brexit referendum, a slow recovery from the pandemic and the UK’s exit from the EU all contributed to the underperformance of UK trade. (more…)
Charlotte Humma February 15th, 2024
Posted In: Uncategorised
4 January 2024
Guest author David Henig is Director of the UK Trade Policy Project at the European Centre for International Political Economy (ECIPE). He has written extensively on the development of UK Trade Policy post Brexit, in the context of developments in EU and global trade policy on which he also researches and writes.
There was relief for Europe’s automotive sector at the start of December when the UK and EU agreed to maintain current product specific rules of origin for electric vehicles within the Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA) until the end of 2026. A scheduled intermediate stage of tightening on the way to even more stringent final rules to take effect from January 2027 was abandoned. Industry in both the UK and EU had been warning of potential 10% tariffs without an agreement and welcomed the move.
At the most basic level, this extension demonstrated that the UK and EU can find ways to improve their trading relationship. This had previously been shown with the agreement of the Windsor Framework to supplement the Northern Ireland Protocol to the Withdrawal Agreement, reached in February 2023, as well as full UK accession to the Horizon science research programme, scheduled to take effect at the start of 2024. Many commentators on both sides had doubted such progress would be possible at the start of the 2023.
With the TCA being the most valuable preferential trade arrangement to both the UK and EU, any indications of a better relationship should come as a relief. According to a November European Commission report “on the Implementation and Enforcement of EU Trade Policy”, in terms of EU preferential trade deals 22.5% of their value in goods is with the UK, rising to 46% for services. Meanwhile, despite the UK government’s aspirations for Global Britain, over 40% of its total trade remains with the EU.
Details of the negotiation and agreement over electric vehicles suggest however that it would be premature to expect plain sailing from this point onwards. There were suggestions in October that the broad principles of an extension for electric vehicles had been agreed, yet there were concerns on the EU side about whether this should be done legally inside the TCA or through a separate instrument. Final text which includes a prohibition of further extension showed a certain sensitivity in Brussels. In time this restriction could itself by renegotiated, but a marker not to do so has been laid.
For the EU, sensitivity is almost certainly based on their continued fears of a Brexit UK still expecting the market access of a Member State, in particular in areas of its specific interest. Experience was further that this attitude came with petulance and aggression from UK negotiators when not granted, in public and possibly to a degree inside negotiating rooms. These fears and memories should be of particular concern to a Labour Party committed to seeking TCA enhancements, particularly in terms of mutual recognition through agreements on food and drink, and professional qualifications. While the EU has shown a willingness to talk and does have its own interests, it should be obvious that no deal will be straightforward particularly if the EU is concerned about protection against future UK governments.
Meanwhile UK and EU automotive sectors face the challenge of being some way behind their Chinese competitors. For the time being, with this extension, and with the EU’s investigation into subsidies that may lead to countervailing duties, the industry is being given some time to catch up. There is clearly the expectation of this happening in the next three years, something which industry experts are already suggesting to be optimistic.
Extending and changing preferential trade agreements is never an easy matter, even between the friendliest trade partners. Particular circumstances of the UK-EU relationship make this even more difficult. Given such a background, one should probably see progress this year including on electric vehicles as being as good as it could get. That can perhaps be the foundation for a new approach, in a new year, and possibly even a new UK government, but they would do well to take nothing for granted.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the authors alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher January 4th, 2024
Posted In: Uncategorised
Share this article: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 13 December 2023
13 December 2023
James Harrison is Professor in the School of Law at the University of Warwick. Emily Lydgate is Professor in Environmental Law at the University of Sussex and Deputy Director of the UK Trade Policy Observatory (UKTPO). Ioannis Papadakis is a researcher at the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy (CITP) and a Research Fellow in Economics. Sunayana Sasmal currently serves as a Research Fellow in International Trade Law at the UKTPO. Mattia di Ubaldo is Fellow of the UKTPO and Research Fellow in Economics of European Trade Policies. L. Alan Winters is Founding Director of the UKTPO, Co-Director of the CITP and Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex.
In answering this important question, different disciplinary approaches have emerged as have a range of different and sometimes contradictory findings. At the moment, scholars from the different disciplines are not talking to each other about the implications of this. The authors of this blog suggest it is vitally important that they begin to do so.
Trade agreements around the world increasingly include environmental and labour provisions. Their presence attests to policymakers’ recognition that trade agreements cannot simply focus on economic issues. They should also address environmental and social concerns. But the existence of these provisions on paper is not itself a cause for celebration. Such provisions are only meaningful if they have positive outcomes in reality – if they, for instance, lead to decreased carbon emissions or enhanced conditions for workers.
Different methodological approaches to researching this issue have come to different conclusions about their real-world impact. First, quantitative studies, largely undertaken by economists, have tended to identify significant and generalised positive impacts for at least some provisions.
On the environmental side, one early influential study found that EU FTAs with environmental provisions improve environmental conditions in countries with strong civil societies. It also concluded that US FTAs are effective during the negotiation period in improving the environmental policy environment of partner countries. Another, covering 680 PTAs with environmental provisions, found that environmental provisions can help reduce dirty exports and increase green exports from developing countries.
In relation to labour provisions, one study found that the likelihood of a state fully protecting workers’ rights rises by 10% once it has signed an FTA with the EU which contains labour provisions. Another study found that labour provisions had a positive impact on (particularly female) labour force participation rates (although not on other labour rights).
On the other hand, more recent work, carried out with more advanced statistical techniques and more granular data on both the content of FTAs and the environmental outcomes, tends to find only mixed evidence: some specific provisions on greenhouse gases appear to be effective, but results are not consistent across models. No significant effects are found for labour provisions. Some recent work has also focused on specific outcomes produced by environmental provisions. Thus, one study, focused on deforestation, found that environmental provisions are effective in limiting deforestation following the entry into force of FTAs, but only because FTAs without such provisions increase deforestation and the provisions offset this.
There is also some indirect evidence of the effects of FTAs. One study suggests a positive relationship between domestic environmental legislation (not environmental outcomes) and preferential trade agreements with environmental provisions, while another finds that FDI is deterred if FTA labour and environmental provisions have a higher degree of legalization. However, others suggest that such provisions might increase the costs of trade and production.
To sum up this first side of the literature, quantitative studies tend to suggest that some generalisable, although often limited, effects can be ascribed to labour and environmental provisions in FTAs. Across a wide range of different agreements, these studies suggest that some changes will happen as a result of the presence of some types of provisions – for instance that deforestation will be limited or domestic environmental legislation will be signed.
Legal scholars are often puzzled by these results. Environmental and labour provisions take multiple forms in different FTAs and are often not the kind of binding and enforceable provisions that are expected to produce significant results. In high-level summary, trade and sustainable development (TSD) chapters (as found in EU FTAs) and equivalent provisions in other FTAs often consist of ‘best endeavours’ clauses that commit parties to work towards high standards; cooperation on thematic issues, including through upholding agreements such as conventions of the International Labour Organization or the Paris Agreement; and obligations not to reduce levels of protection, often described as non-regression clauses.
Much debate has focused on whether these non-regression clauses should be tied to sanctions, as the US has done, and more recently the UK, Australia and New Zealand. In contrast, EU FTA commitments emphasize implementation through stakeholder dialogue of bespoke committees, such as a Civil Society Forum and Domestic Advisory Group. The EU has unveiled a plan for a limited increase in the use of sanctions in TSD chapter enforcement, and the USMCA has introduced new and innovative forms of labour rights enforcement.
Enforcement mechanisms remain an important focus for legal scholarship, as does the influence of FTA negotiations in changing domestic environmental and labour laws. However, focusing solely on treaty texts and the strength of the bodies that potentially enforce them, doesn’t provide a full account of the impacts of particular provisions.
Qualitative studies have been used by political scientists, geographers, business and socio-legal scholars to attempt to understand how obligations contained in treaty texts have translated into changes in labour and environmental outcomes. Such studies have generally involved case study methodologies and techniques such as in-depth interviews, focus groups and participant observation that allow deep exploration of the causal effects of certain sustainability provisions.
Most of the detailed studies have focused on EU trade and sustainable development (TSD) chapters and the labour standards provisions therein – although as environmental provisions are implemented and enforced in the same way, there are some learnings from these studies on the environmental side. Case studies on impacts in the EU’s FTAs with the CARIFORUM countries, Colombia, Korea, Moldova and Peru have found little or no evidence that the existence of TSD chapters led to improvements in labour standards governance, nor that there were significant prospects for longer-term change. Less robust studies of labour standards provisions in individual US agreements have led to similar conclusions. Positive impacts have been found to occur only in very limited scenarios when accompanied by specific actions by key actors (government officials, civil society actors, trade unions etc.), in relation to specific trade agreements where those issues became politically contentious, such as prior to the ratification of the EU-Vietnam FTA.
Overall, the findings of the studies presented here are very different. But their methodological strengths and weaknesses can also be contrasted. Quantitative studies are able to consider labour and environmental provisions across a wide range of agreements, thereby providing information about general tendencies. But these studies, particularly the earlier ones, are less compelling on the issue of causality. While sustainability provisions are posited as a likely cause of improvements in environmental and labour protection, there are generally weak attempts to substantiate causal links. The few studies that do make serious efforts to identify causal (and unbiased) links, tend to come up with many fewer positive effects. Most importantly, however, they all lack a convincing narrative about the mechanisms leading from FTA provisions to impacts on the ground.
Qualitative studies take causality seriously and can give detailed answers on the direct causal questions of how and why sustainability provisions have or do not have effects. On the other hand, they are weaker when it comes to generalisability; reliance on individual case studies leaves qualitative studies open to accusations that they have missed the ‘bigger picture’.
Scholars who have adopted these different approaches should come together to try to understand the rationale for these different findings and to promote better understanding of their respective research methods. Drafting this blog challenged some of our assumptions about how different disciplines tackle research questions, and facilitated our understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of our research approaches.
But this is not only an academic question. Understanding these methodological strengths and weaknesses has implications for policy making, as correct and full facts are essential to make good policy. For instance, there are policies with unintended consequences that can be identified by talking to people. When these are not considered, empirical analysis may lead to misleading policy prescriptions, even if the effects it estimates are precise, causal and generalisable.
Policymakers need to understand the effects of labour and environmental provisions if they are to take the right kinds of actions to promote better social and environmental outcomes through trade agreements. The authors of this blog all agree that there is a big difference between (1) telling policymakers they can achieve meaningful change through inserting environmental or labour provisions into trade agreements and (2) that to be effective, they must think very carefully about both the design of those provisions and how they will be taken up and utilised by key actors thereafter.
A broad account of how the disciplines can work together might go something like this: Economic studies identify FTAs where the correlation between environmental or labour provisions and positive outcomes appears to be high. Legal scholars bring a detailed understanding of the typology of FTA environmental and social provisions within these FTAs, using this to further refine economists’ findings about causal mechanisms. Political scientists, geographers, business, and socio-legal scholars interrogate how issues such as relationships, power asymmetries, access to information and access to resources shape the effectiveness of the environmental and social provisions in practice.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the authors alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher December 13th, 2023
Posted In: UK - Non EU, UK- EU
Tags: Environment, environmental law, EU, FTAs, labour standards, Trade agreements, trade policy
20 October 2023
 Erika Szyszczak is a Professor Emerita and a Fellow of the UKTPO. She was the Special Adviser to the House of Lords Internal Market Sub-Committee in respect of its inquiry into Brexit: competition and state aid, and has previously acted as a consultant to the European Commission. She specialises in EU economic law. She is currently working with the European Judicial Training Network on developing training courses for national judges in EU competition law.
Erika Szyszczak is a Professor Emerita and a Fellow of the UKTPO. She was the Special Adviser to the House of Lords Internal Market Sub-Committee in respect of its inquiry into Brexit: competition and state aid, and has previously acted as a consultant to the European Commission. She specialises in EU economic law. She is currently working with the European Judicial Training Network on developing training courses for national judges in EU competition law.
On 3 October 2023 the Council and the European Parliament reached provisional political agreement on an Anti-Coercion Instrument (ACI).[1] It is the latest legal trade measure contributing to the developing economic statecraft of the EU as part of the Open Strategic Autonomy. The tipping point for the EU to consider an extra method to address trade distortion occurred when China imposed trade restrictions on Lithuania after Lithuania improved trade relations with Taiwan. Lithuanian companies found that they could not renew or conclude contracts with Chinese firms, shipments were not being cleared and customs paperwork was held up. The ACI is portrayed as a deterrent device, discouraging third states from targeting the EU and its Member States with economic coercion through measures affecting trade or investment. It is another example of how the EU is forging a leadership role in developing new economic trade rules in a fragmented global trading world, by stealing a lead in the narrative on what is, and what is not, acceptable trade policy.
The European Commission proposed the ACI in the form of a Regulation on 8 December 2021 at the request of the Council and the European Parliament. The European Parliament Committee on International Trade adopted amendments to the proposal on 10 October 2022, and in the plenary session confirmed the Parliament’s negotiating mandate on 19 October 2022. The Council agreed its negotiating position on 16 November 2022.
The tipping point for the EU to consider an extra method to address trade distortion occurred when China imposed trade restrictions on Lithuania after Lithuania improved trade relations with Taiwan. Lithuanian companies found that they could not renew or conclude contracts with Chinese firms, shipments were not being cleared and customs paperwork was held up.
The Legal Base for the ACI is Article 207(2) TFEU:
“The European Parliament and the Council, acting by means of regulations in accordance with the ordinary legislative procedure, shall adopt the measures defining the framework for implementing the common commercial policy.”
This is trade legal base for a measure designed to enhance EU economic and political resilience. The European Parliament Committee on International Trade adopted amendments to the proposal on 10 October 2022, and in the plenary session confirmed the Parliament’s negotiating mandate on 19 October 2022. The Council agreed its negotiating position on 16 November 2022.
The ACI defines economic coercion as when a non-EU country attempts to pressure the EU or a Member State into making a specific choice by applying, or threatening to apply, trade or investment measures. In the European Parliament Briefing ‘Proposed anti-coercion instrument’ different types of economic coercion are identified:
Once notified of an alleged act of economic coercion the European Commission must investigate within 4 months. The European Commission report will be sent to the Council which then has between 8 to 10 weeks to decide, by a qualified majority vote, whether the complaint of economic coercion exists. The first response will be to engage in dialogue to persuade the authorities of the non-EU country to stop the acts of economic coercion. If diplomacy fails, the EU has a range of countermeasures it can apply with the consent of its Member States. These include restrictions in trade of goods and services, intellectual property rights and foreign direct investment, imposing constraints on access to the EU public procurement market, capital market, and authorisation of products under chemical and sanitary rules. The European Commission has 6 months to set out the appropriate responses, whilst keeping the European Parliament and the Council informed at all stages.
The ACI is a new legal development in international trade law. It has been developed in response to activities deployed by China and the US which threaten EU security. The ACI is another example of how the UK, post-Brexit, may be the target of EU trade defence instruments.
Why does the EU need the ACI? The European Commission justifies the measure by arguing that new forms of economic coercion are not addressed by the existing conventional trade defence measures of the EU (for e.g. anti-dumping).
The concept of economic coercion set out in the ACI is not caught by current WTO rules. Even if the threatening behaviour could be brought within the existing WTO agreement, the stymied appellate process makes enforcement difficult.
However, the ACI is not a rapid defence trade mechanism. In fact, an EU firm or sector could suffer irreparable damage in the time it takes to activate and use the ACI. It may also encourage third countries to develop their own trade defence tools which are more effective than the ACI in responding to escalating situations.
[1] The European Commission proposed the ACI in the form of a Regulation on 8 December 2021 at the request of the Council and the European Parliament. EUR-Lex – 52021PC0775 – EN – EUR-Lex (europa.eu). The European Parliament Committee on International Trade adopted amendments to the proposal on 10 October 2022, and in the plenary session confirmed the Parliament’s negotiating mandate on 19 October 2022. Procedure File: 2021/0406(COD) | Legislative Observatory | European Parliament (europa.eu). The Council agreed its negotiating position on 16 November 2022. pdf (europa.eu). The Legal Base for the ACI is Article 207(2) TFEU: The European Parliament and the Council, acting by means of regulations in accordance with the ordinary legislative procedure, shall adopt the measures defining the framework for implementing the common commercial policy.
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Jessie Madrigal-Fletcher October 20th, 2023
Posted In: Uncategorised
Share this article: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

 Michael Gasiorek is Director of the UK Trade Policy Observatory and Co-Director of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy. He is Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex Business School. Justyna A. Robinson is a Reader in English Language and Linguistics at the University of Sussex and a Director of Concept Analytics Lab.
Michael Gasiorek is Director of the UK Trade Policy Observatory and Co-Director of the Centre for Inclusive Trade Policy. He is Professor of Economics at the University of Sussex Business School. Justyna A. Robinson is a Reader in English Language and Linguistics at the University of Sussex and a Director of Concept Analytics Lab.
In early 2023, the Labour Party launched a National Policy Forum. It comprised a series of public consultations across six core policy areas, with the stated aim of helping the Labour Party to ‘build their policy platform’. A key part of the consultation process was to invite written submissions on these policy areas. One of the six policy areas was entitled Britain in the World, (to which the UKTPO/CITP also responded), which posed a set of seven questions all of which related to trade and trade policy.
The consultations were due to lead to a set of policy documents to be agreed in July 2023. With any consultation exercise, including those undertaken by the UK Government on the UK’s Free Trade Agreements, it is hard to know how seriously the consultation is being taken and which if any of the diverse views and responses are being listened to, and how selectively. Consulting with stakeholders and members of the public in the formulation of policy are important if taken seriously, and so consultations such as this are, in principle, welcomed.
So, on the eve of the Labour Party conference, we have analysed all the submitted responses to identify the key issues raised. There were 310 responses submitted which varied considerably in length. Most submissions were less than 500 words, but some were as long as 10,000 words. It is important to note that the consultation was open to anybody: individuals as well as organisations and companies. The chart below shows that 35% of the submissions were submitted by non-Labour party members (labour guests).[1]

Analysing the data is a challenge because the responses vary enormously in length and scope – with some private individuals submitting short sentences on a couple of issues, to larger organisations and companies submitting lengthy responses. Fortunately, there are tried and tested methods (and smart) software which provide a means for using corpus and natural language processing techniques for the analysis of such textual responses and controlling for different lengths of responses, so that individual lengthy responses do not dominate the analysis.
A key aspect of the analysis is to identify the frequency with which submissions raise particular issues. This is done by comparing the frequency of given words or groups of words in the submissions, relative to the frequency with which those words would appear in ‘normal’ usage. Hence words that appear relatively more frequently are those that prima facie raise issues that the respondents care about. In the jargon, this is called the ‘keyness’ score. We also need to control for the fact that certain terms may appear more frequently in individual responses. So, we want to be able to identify how often an issue is raised but to adjust for those issues being raised frequently in a small number of responses. This is done by producing something called the ‘average reduced frequency’ (ARF).
Consider the chart below. This gives the ARF score for the top 10 identifiable trade issues raised in groups of up to three words[2]. We see that the issue of trade and human rights is the primary concern, on average across the responses. Care has to be taken in interpreting the height of the bars – just because a bar is twice as high does not mean that the issue was perceived as twice as important. Nevertheless, it is clear that human rights were perceived as considerably more important than supply chains and economic growth.


Relatedly, if one takes the importance of individual words, the word ‘promote’ has a high ARF score. On its own, it is not clear what the respondents want promoting, and so we look at the collocation of words. This identifies that the key objective here was to promote growth, followed by rights, values, trade, and development in order of importance. Another word with a high individual score was ensure which co-occurs most with security (of supply chains), rights, and access (markets, supply chains), suggesting that these are of high importance for trade policy.
Of course, the frequency of some of these words will have been driven by the specific questions posed by the consultation exercise, as given above, which specifically asked about growth, supply chains and human rights for example. Even so, the rankings are significant as they indicate which of these issues appear of greater concern to respondents.
More depth in the analysis can be obtained by considering the nature of the responses to the individual questions posed. Hence, the responses pertaining to the role of international trade in promoting domestic economic growth, boosting jobs and driving up wages illustrate different perceptions of what trade policy is for. While some responses highlighted the role of trade in boosting productivity, innovation and access to supply chains, as well as emphasising trade with the EU; others focused on the role of trade (deals) in building relationships, soft power, and trust with third-party countries. Additionally, some demonstrated concern for objectives which are not focused on economic growth and economic efficiency such as the regional dimension, worker and human rights, or environmental protection.
With regards to the regional dimension, there is a clear message that international trade, especially services trade as well as ‘green’ trade, could and should be used to reduce regional disparities but that this also requires much more substantial investment in infrastructure and transport networks, as well as policies to mitigate negative impacts if it is to be successful. There was general acceptance of the importance of building more resilience in supply chains with a focus on the need to build trust with partner countries and reorienting supply chains to more trusted countries as well as protecting cyber-security. Interestingly, there was an overlap here with environmental and rights concerns with several respondents calling for more due diligence requirements in supply chains and moving to net-zero supply chains.
Environmental protection and cognate terms such as green technology, carbon emissions, energy, due diligence come up widely in the responses with widespread support for a better environment and net zero, even if it means renegotiating existing deals. Interestingly, the desire to use trade deals to lead to better outcomes in these regards does not pertain just to the UK, but that the trade deals should be used to influence and change practices in partner countries.
The responses highlight the importance of taking into account how trade may negatively impact a range of outcomes, be this with regard to the environment, regions, agriculture and animal welfare, older workers, disabled workers, or women. However, such concerns did not lead to opposition to trade deals, but rather to suggesting that (a) consideration of such impacts should form a (more) explicit element in the evaluation of proposed trade deals; and importantly (b) that there should be much more widespread inclusive consultation processes with affected groups, sectors, and regions in the formulation of trade policy and the negotiation of agreements.
Given the range of questions posed in the consultation exercise, it is perhaps not surprising that there is considerable heterogeneity in the answers. One clear message, however, which emerges is the recognition that trade is good for growth and an important element in raising productivity, but that at the same time, trade policy needs to be value driven. While these are not necessarily mutually exclusive there are trade-offs in trying to meet all the objectives. Hopefully publication of a trade strategy by the Labour Party may provide some insights on their approach to those trade-offs, and maybe the forthcoming conference may also shed some more light.
[1] Categories as defined by the Forum, see bottom of this page for all categories: https://www.policyforum.labour.org.uk/commissions/britain-in-the-world
[2] Note that we have excluded here terms that came up but do not, of themselves, shed meaningful light on trade issues, such as ‘UK government’ or ‘Labour Party’
Disclaimer:
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author alone and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the University of Sussex or UK Trade Policy Observatory.
Republishing guidelines:
The UK Trade Policy Observatory believes in the free flow of information and encourages readers to cite our materials, providing due acknowledgement. For online use, this should be a link to the original resource on our website. We do not publish under a Creative Commons license. This means you CANNOT republish our articles online or in print for free.
Charlotte Humma October 6th, 2023
Posted In: Uncategorised